Jun 8, 2023
PLC Programming Languages
Jun 18, 2018
PLC Programming for Tank Level Measurement using Ultrasonic Sensor
In our earlier post, we saw the PLC Logic for Auto Filling of Tank using digital inputs for LOW and HIGH-Level signals.
PLC Programming for Tank Level Measurement Using Ultrasonic Sensor
First of all, we need to choose the Ultrasonic/Capacitive level sensor according to our tank level height. The sensor will give a 4-20mA signal to PLC and accordingly, we will calculate the level in the tank.
PLC Logic Development:-
Now, we need to connect the analog input from the ultrasonic sensor to PLC, we have already told that in our earlier post. You can see it here.
After that, we have to write SCL (scaling instruction) in the PLC to convert the value received by PLC to the scale we want.
So that when the Ultrasonic sensor will give 4mA signal then the level in the tank will be zero and when a signal of 20mA will be received then the level in the tank will be 5000cm.
In SCL instruction, we have to define the scaling parameters in some D:-
D200 - 0
D201 - 0
D202 -5000 (hexa)
D203- 0FA0 (hexa)
Here the value 0 to 0FA0 received by PLC will be scaled to 0 to 5000 (our tank height).
Now in this PLC Program we have kept the low level at 2500cm and the high level at 4600cm. You can download the PLC program from below, we have built the PLC Program using the Omron CX-supervisor software. Both the .cxp and .pdf files are included.
Download PLC program for Tank Level Measurement.
Hope you like this PLC program on controlling your Tank according to the measurement using an Ultrasonic sensor. If you face any problem with this PLC Program or want any modification then write us in the comment section.
Mar 23, 2018
Best PLC Ladder Programming Books
If you are new to PLC programming or want to enhance your programming skills, then you really have to work hard. For this, you will need a good mentor and good books for your help.
1. Programmable Logic Controllers with ControlLogix by Jon Stenerson :
Programming Controllogix Programmable Automation Controllers strength is its breadth and depth of coverage, taking the reader from an overview of the Programmable Logic Controllers through ladder logic, structured text, sequential function chart, and function block programming.

According to one of its reader, this book is must read for beginner with no ladder logic experience. See more Info
2. Introduction to PLCs, Second Edition by Jay F. Hooper :
This book is oriented to the people that work on and troubleshoot PLCs on the factory floor. It is directed at the actual problems and conditions that will be encountered within a realistic setting.

This book takes you from the beginning of understanding to the most complex problems helping you understand every step of the way. See more Info
3.Programmable Logic Controllers Textbook with PLC Stimulation Software by Max Rabiee:
Programmable Logic Controllers emphasize the practical use of the PLC in the process and industrial control systems. The textbook begins with the basics of what a PLC is and does, then guides students through the fundamentals of programming the device.
The wiring and programming of a PLC are covered thoroughly, using numerous examples. A supplemental laboratory manual provides a wealth of hands-on activities that will help students practice and hone their PLC programming skills.

It also includes a CD-ROM containing LogixPro simulation software with a textbook. LogixPro is the ideal tool to facilitate student learning of the fundamentals of RSLogix ladder logic programming. See more Info
Hope you will like these books and if you have any other good suggestions, please comment below.
Mar 4, 2018
Conzerv Energy Meter EM6436 Modbus Communication and Connection Diagram
Conzerv has a range of EM series Energy meter and there are various different models available for your different need and according to the application. Conzerv Energy meter comes with and without Modbus communication feature, so be sure when selecting Energy Meter according to the application. If you want to communicate it with PLC then make sure that it is MODBUS Enabled.
The EM series Power meters offer complete load management facilities in a compact package. If you like to see more such posts, please subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
How to check whether Conzerv Energy meter is MODBUS enabled?
1) First of all, check that terminals 7 and 14 of meter does not have black dot mark, if there is a black dot market on it then it is not MODBUS enabled.
2) Secondly, check that on the front left bottom side RS485 is written and the color of the dot before this, if the color of the dot is white then it is MODBUS enabled and if it is black then it is not MODBUS enabled.
All Conzerv Energy and power meter come with different function keys in the front side for easy set up of the parameters and also some models have TURBO key through which you can directly go to set up mode.
Connection Diagram of Conzerv EM series Energy Meter
NOTE:- Click on the picture for a clear view.
In the above picture, you can see the connection of energy meter. Connect your meter accordingly. The meter has 3 line display and display the parameters sequentially one by one i.e their name and value one by one.
Now the main question is how to communicate Conzerv Energy Meter in MODBUS?
So here is the answer, first of all, make proper hardware connection of MODBUS accordingly that is connect positive of PLC RS485 port with terminal 7 and negative of PLC RS485 port with terminal 14 of Conzerv Energy meter.
Now you have to make PLC program accordingly, generally, in MODBUS we read the parameters like a line to line voltage, frequency, current, power factor etc. Each parameter has its unique address in the energy meter and it has to be read through the query in MODBUS.
Make sure to set the node id, baud rate, parity in yours Conzerv energy meter properly using the setup mode.
You can download the address map of Conzerv Energy meter EM series from here .
Click here to download.
Now the question is How to read data from Conzerv Energy meter in MODBUS using OMRON PLC.
You can review the Omron PLC MODBUS communication from here.
So here is the Data format to read:- 01 03 04 (address - 1) 02
Make sure to subtract 40001 from the address.
Response from energy meter:- 01 03 00 05 0486 9042 4800
Here the value of the parameter in response is 4248, remember that the response of Conzerv Energy meter is always in float, so make sure to convert it accordingly. For example in the above response, the value returned by EM is 4248 in float which is equal to 49.98 in decimal and it is the value of frequency.
So accordingly you can read others parameter too by using the above query format. Hope you like this article and if you do, do not forget to subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
Feb 19, 2018
Auto Mains Failure PLC Program using Omron PLC
"Auto Mains Failure System" is Employed for Auto startup of the DG when the mains supply fails. This is a very common system and is the first step in DG synchronization. Here we will see that what is the basic concept in AMF? What hardware is required to set up AMF and how PLC Programming is done.
First of all let us understand what is AMF?
Generally, all the major industries/companies/institution have the DG for power backup, but when main power is cut off, someone has to go to start the DG and this takes time and also a man has to be kept for this purpose. So to eliminate this process PLC panel is installed to Auto start the DG when main power fails. Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email for more such tutorial.
Working of Auto Mains Failure
When the main power goes, a signal is received to PLC and after 2 minutes DG starts. When the main supply fails signal is received by PLC then after a delay time (can be from 1 to 2 minute), the output for ACB/Contactor of DG is ON and DG starts automatically. Also, the ACB/Contractor of the main transformer if sent OFF command.
When main power comes then the signal is again sent to PLC and PLC off the ACB/Contactor of DG and after 2 seconds it on the ACB/Contactor of the main transformer and after 30 seconds it off the DG. DG is sent OFF command a little late so that the load born by DG for a long time can be compensated by running at no load for some time.
NOTE:- In 'No' condition, the ACB/Contactor of both DG and Main transformer should be ON.
So this is the main concept in DG AMF system.
In a simple system, there are generally 4 inputs and 4 outputs.
Inputs:-
1. DG ACB/Contactor close feedback.
2. Transformer ACB/Contactor close feedback.
3. Transformer Voltage Available.
4. DG Voltage Available.
Outputs:-
1. DG start.
2. DG Stop
3. DG ACB/Contactor close.
4. Transformer ACB/Contactor close.
For your better understanding below is the sample program. If you have any doubts then just write in comments and we will get back to you. Download the PLC Program for AMF:- Click here to Download.
Hope you like this article, if you do comment below and share it on social media. Hope to see you on next article.
Nov 7, 2016
PLC Programming For Counting Encoder Pulses
 Encoder is mainly used for feedback purpose to know the position and distance measurement in Industrial applications. But before going in to the PLC Programming we should be familiar with Types of Encoder , Interfacing of Encoder with PLC.
Encoder is mainly used for feedback purpose to know the position and distance measurement in Industrial applications. But before going in to the PLC Programming we should be familiar with Types of Encoder , Interfacing of Encoder with PLC.
PLC Programming For Counting Encoder Pulses / Feedback:-
Actually encoder is mounted on the shaft whose position we want to determine or want to monitor its value. Encoder have some PPR and they gives accordingly that number of pulses in one revolution.
Note:- The coupling of encoder with shaft should be done properly for accurate measurement otherwise the efficiency will decrease or it can even destroy.
PLC Logic Development:-
Now we will see the step by step detail for making the PLC Program. First of all we have to decide the condition that when should the counting start i.e when the pulses given by Encoder will be counted. Generally we want this at the auto-cycle start , So here we are considering at Auto Bit ok condition , however it can be done as per application requirement.
We here are considering the example of Omron PLC CP1H, in every PLC there is a Instruction for counting the high speed pules, In Omron it is PRV , so we will write PRV Instruction.
In PRV we have to define the port number where we have connected the Encoder and control Data. After that the value(encoder pulse value) will coming in one Data Register of PLC.
Now we have to decide as what to do this value. Let us take one example , suppose our encoder is of 360PPR i.e it will give 360 pulses in one revolution, Encoder is connected to motor shaft which is driving a conveyor and after every ever 300mm conveyor will stop and a cylinder will come down to cut.
So first we will calculate that in 1 revolution of encoder how much the conveyor moves.
If in 360 pulses conveyor moves 100 mm then we find that , for 1080 pulses of encoder conveyor moves 300mm.
Note:- Settings in the CX-Programmer.
So, after every 1080 pulses we will stop the motor and on the cylinder output and simultaneously reset the Encoder value, and continue this process. We will compare the Encoder Pulse value with the 1080 and at when they equal, motor stops, cylinder down and encoder value reset and motor again runs.
We have made the PLC Program accordingly. See the PLC Program below, we have included both the .cxp and .pdf files.
Download the PLC Program.
Also if you face any problem then you can leave us a comment. You can subscribe to get all related PLC Programs, SCADA Tutorials, HMI, VFD Installation related articles in yours inbox. Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email for more such articles.
May 24, 2015
PLC Logic Auto-Filling Tank - Free PLC Programming
 Almost in all of the industries Tanks are there for storing up the liquid,chemicals or there are overhead water tank for the water supply in plant.Generally for overhead tank a pump is there for filling of the tank or in other cases also there is a motor/pump for filling purpose of tank. So if the filling of tank is a manual process then a operator has to be employed for the ON and OFF process of the PUMP.
Almost in all of the industries Tanks are there for storing up the liquid,chemicals or there are overhead water tank for the water supply in plant.Generally for overhead tank a pump is there for filling of the tank or in other cases also there is a motor/pump for filling purpose of tank. So if the filling of tank is a manual process then a operator has to be employed for the ON and OFF process of the PUMP.
PLC Logic for Auto-Filling of Tank - Free PLC Programming
So, as told above if the process of filling is manual then we have to assign this task to a operator to ON the pump when the Tank empties and OFF the pump when the Tank fills. But in today's scenario all the process are automatic. So today we will discuss the automatic filling of tank and automatic ON-OFF of pump according to tank level. We will build a PLC Logic for this complete application. To write the PLC Program for this process we should understand the logic first.
The PLC Logic will be like following
To monitor the level in tank we can either use a Ultrasonic/Capacitive level sensor which will give analog input to PLC OR we can just put two sensor one at HIGH level and another at LOW level and they will give the signal to PLC for HIGH and LOW level respectively.
When the level will be LOW in tank then the PUMP will start and the filling of tank will start and when the level reaches the HIGH level the PLC will receive the HIGH level signal and the PUMP will stop, so the filling of tank will stop. When again tank empties the PUMP will start on its own and the process continues.
Generally the On and OFF of pump at two levels is a task that requires little intelligence. Suppose the height of tank is 5000cm then the low level should be around 2000cm and high level at 4600 cm. It is done because if for example the low level is set at 300cm hen the PUMP will start at 300 cm and suppose if at the same time the consumption rate increases than the supply of PUMP then the tank will empty. So keep in mind this thing while setting the LOW and HIGH level in Tank.
Well there is no need to install a separate PLC for this small application, as almost all the major industries have the PLC installed so the logic can be built in that existing PLC and thus there will be savings.
PLC Logic Development
Here we will take example of Omron PLC and build the PLC logic using CX-Programmer.
INPUTS :-
0.0-------------------------------------------------------------- Low level Signal
0.1-------------------------------------------------------------- High Level Signal
OUTPUTS:-
100.0 ------------------------------------------------------------ PUMP ON
Here we have build the PLC Programming using the digital Inputs, but the same can using the Ultrasonic/Capacitive Level sensor and taking the Analog input to PLC. You can download the PLC program from Below.
Download PLC Programming logic of Auto Filling Tank.
We have attached both .pdf and .cxp files so that who don't have CX-Programmer software can still view the logic and understand the PLC Logic.
We will also build the PLC logic using the Analog input to PLC, so keep visiting and you can subscribe to Automation Talk for such more PLC Programming examples, SCADA tutorials, VFD applications and HMI Programming.
If you have any doubts regarding this PLC Program then you can write in the comment section below and we will get back to you ASAP. Don't forget to Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
May 9, 2015
Using PLC Clock Time in Omron PLC Programming
Almost every plc have the clock function that is we can get the time value in the plc data words. We can synchronize the plc time with the system time at the time of program downloading. PLC stores the value of time , day , Month and year in its internal data words. We already have discussed about the plc internal words.
Reading the Year/Month/Day/Time Value in PLC :-
Many a times while developing the plc logic sometimes it is required to use the time in program to perform a particular function. Also there must be situation when we need to operate a particular device on a Specific date and time. So all these things are possible in PLC , all we need is to find out the plc system words where these values are stored.
Here we will see the example of Omron PLC. One thing we should keep in mind is that the plc must have battery installed so that real time monitoring of Date and Time is possible. In omron PLC there are 4 system words for storing the value of Year,Month,Date,hour,minute and second.
A351 to A354 are the system words in Omron PLC which stores these values. See below for the complete detail.
A351.00 to A351.07 Seconds: 00 to 59
A351.08 to A351.15 Minutes: 00 to 59
A352.00 to A352.07 Hour: 00 to 23
A352.08 to A352.15 Day of the month
A353.00 to A353.07 Month: 01 to 12
A353.08 to A353.15 Year: 00 to 99
A354.00 to A354.07 Day of the week
00: Sunday, 01: Monday, 02: Tuesday, 03: Wednesday 04: Thursday, 05: Friday, 06: Saturday
So by seeing the above values in these system words we can get the exact Date and Time. We can compare the values in these words with our pre-defined DM words and make the plc logic accordingly. Also when we download the program in plc then for the first time we have to synchronize the plc clock with our system clock. See below picture.

Now for example take a situation that we need to operate a particular output to be on 8 pm 20 Dec 2012 and be on afterward. So for this we will use compare instruction and compare the A351 with #0 and A352 with #2020 and A353 with #1212 and when these conditions gets satisfies the output will be on. If you see properly then these condition will be satisfied exactly on 8 pm 20 Dec 2012.
We hope that this plc tutorial will help you to use the plc clock time in developing plc logic . If you still face any problem you can write us in comment section. Also you can subscribe to get all latest updates in plc programming.Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
Mar 1, 2015
PLC Programming for Dancing Light - PLC Programming
Many users mailed us for making the PLC program for the dancing light, so here we will see the PLC Logic for making a fancy light decoration system.
PLC Programming for Dancing Light - PLC Programming
Here in this PLC Program, we are considering six numbers of LEDs, 1 start push button, 1 stop push button, and 1 selector switch. We will write the PLC program for 2 different modes i.e the LEDs will glow in two different patterns.
Recommended Article: Free PLC Software's for Ladder Logic Programming
Mode 1 Pattern of LED Glowing:- While writing this PLC logic we have made the PLC program in such a way that when we will push the Start button then LED 1 will glow after 1 second LED 2 will glow and again after 1 second LED 3 will glow and so ON and after 6th LED the cycle will start again. The number of LED's can be more as per the need and application.
See the Below table for a better understanding.
Time -----------LED1 ------------LED2---------LED3---------LED4--------LED5------------LED6
T=0sec ---------OFF--------------OFF----------OFF----------OFF----------OFF-------------OFF
T=1sec ---------ON --------------OFF----------OFF----------OFF---------OFF-------------OFF
T=2sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------OFF-----------OFF---------OFF-------------OFF
T=3sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------ON------------OFF---------OFF-------------OFF
T=4sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------ON------------ON----------OFF-------------OFF
T=5sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------ON------------ON----------ON--------------OFF
T=5sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------ON------------ON----------ON--------------ON
and then again the cycle resets after every 6 seconds.
Mode 2 Pattern of LED Glowing :-
In the second mode , which will be on when we will select it by selector switch the LED 1 and LED6 will glow first for 1 second then LED 2 and LED 5 will glow and then LED 3 and LED 4 .
See below table for a clear understanding.
Time -----------LED1 ------------LED2---------LED3---------LED4--------LED5------------LED6
T=0sec ---------OFF--------------OFF----------OFF----------OFF----------OFF-------------OFF
T=1sec ---------ON --------------OFF----------OFF----------OFF----------OFF--------------ON
T=2sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------OFF----------OFF----------ON---------------ON
T=3sec ---------ON --------------ON-----------ON------------ON----------ON---------------ON
And then after 3 seconds the cycle resets.
PLC Logic Development for Dancing Light
INPUTS
0.0 --- Start Push Button -- (NO)
0.1 --- Stop Push Button --- (NC)
0.2 --- Selector Switch --- (1 pole)
OUTPUTS
100.0 ------------- LED 1
100.1 ------------- LED 2
100.2 ------------- LED 3
100.3 ------------- LED 4
100.4 ------------- LED 5
100.5 ------------- LED 6
We have considered only 6 LED here only, however, the PLC Programming can be extended for any number of LED you want, and also the glowing pattern can be changed as you like.
You can download the PLC Program below. We have attached both .pdf and cx-programmer files.
Download PLC Program for Dancing Light.
If you have any queries in PLC Programming, then write in the comment section, or want any PLC program related to Dancing Light then tell us we will make it for you.
Also, you can subscribe to Automation Talk to receive the latest updates for PLC Programming, SCADA Tutorials, HMI Programming, MODBUS and AC Motors.
Oct 29, 2012
Moving Data using MOV Command in Omron PLC
In some projects, it is required to move some particular or any data to data memory of the PLC in ladder programming in Omron. In that case, we can use a simple instruction called MOV which is used to transfers a word of data to the specified word. This data movement command can be used in 3 forms viz. MOV, MOVL & MVN having different movement function as explained below. Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.

Different Types of MOVE Commands
1. MOV: Transfers a word of data to the specified word. Transfers data in Source to Destination. If S is a constant, the value can be used for a data setting.
Syntax: [MOV Source word Destination word]
Example: [MOV D5 D10]
Here data in D5 will be moved to D10.
2. MOVL: Transfers two words of data to the specified words. If S is a constant, the value can be used for a data setting.
Syntax: [MOVL Source word Destination word]
Example: [MOV D15 D20]
3. MVN: Also called Move Not, transfers the complement of a word of data to the specified word. MVN inverts the bits in source word and transfers it to destination word.
Syntax: [MVN Source word Destination word]
Example: [MOV D25 D30]
MOVB and MOVD are also used in transfer of specific bit and digit respectively. To test move command, you can make a simple PLC program as shown in above image and then try moving data using PLC simulator in Omron. You can check and verify it in Memory area.
Oct 12, 2012
Omron PLC Programs Protection from Being Downloaded
Protecting your PLC program from being edited or downloaded is one of the main concern in some of the important project. So if you are not using PLC protection option to set or release PLC password, then you can use a PLC instruction to protect your PLC program from being edited and downloaded. Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.

For protecting our program we use a simple instruction called FUN(49) with AR memory area. Note that this method can not be used for PLC not having AR area. Some example of PLC with AR area are CPM1, C200H, C200HS, C1000H, C2000H, CQM1, C20P, etc. Main function of FUN(49) is to protect the PLC program and when switch to RUN mode it act as monitor mode.
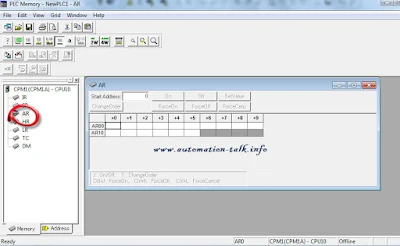
To protect your PLC program just add a NO contact in Rung 0 with address AR10.01 and after that add instruction FUN(49) with below syntax.
Syntax FUN(49) Instruction
[FUN(49) 0 0 #Password]
Below is the sample PLC program for reference.

Aug 6, 2012
How to Configure Modbus Communication in Delta SS2 PLC
Modbus Communication is used in many applications where we need to control VFD from PLC or where we have to read the HMI or SCADA values in PLC. We have seen the Basics of Modbus Communication earlier , also we have understood the Omron PLC Modbus Communication. So we are not going to discuss the basics of Modbus and moving further we will see how to configure Modbus communication in delta PLC.
Understanding the MODBUS Instructions in Delta PLC
In the delta plc we have two instructions for the Modbus communication with any slave. We will consider that Delta PLC is master and there is any other slave device which can be a VFD or HMI. In Modbus communication the Master device always send the query to slave device for reading or writing the registers of Slave Devices. MODWR is the instruction for for writing the MODBUS data.
Syntax :- MODWR S1 S2 N
S1 is the slave address and S2 is the register address of the slave device where we have to write the data and N is the value to write. N can be constant or can be data register address. Let us consider an example - Suppose we want to write to write the H2000 register of slave device with value in D0, slave id is 2. Then we will use the -MODWR K2 H2000 D0.
Reading the Slave data/register in MODBUS Delta PLC :-
For reading the slave register values in Delta Modbus communication we use the instruction MODRD. The syntax is as follows:-
Syntax:- MODRD S1 S2 N
S1 is the Salve address and S2 is the register address of the slave device and N is the number of values to read.
Wiring for Modbus Communication in Delta PLC :-
We have already discussed about the wiring, let us review it once more. In Modbus communication, there are two terminals for on master and slave device. Always connect the + of master with + of slave device and connect - of master with - of slave device.
See :- Delta HMI to Delta PLC Modbus Configuration
We have made a sample program for Delta PLC and delta HMI Modbus communication. You can check it for better understanding.
Download Delta PLC Program
If you like reading our post then don't forget to Subscribe us by email and like us on Facebook.
Jul 21, 2012
Star Delta PLC Program in Delta PLC
Today in this post we will discuss that how to make a star-delta PLC program in the Delta PLC. Star Delta program is required when we run a motor without VFD. Earlier we have discussed that how can we make the star delta program in Omron PLC.
How to Make Star Delta PLC Program :-&
To make a star delta program is very easy. We must know that how to name the input and output coils in delta PLC. In delta PLC inputs are addressed as X and output as Y.
Star delta program making is very easy in Delta PLC. When the start push button is pushed then the main contractor and the star contractor must go ON and at the same time timer should start and after the timer has completed the pre-set time the Star contractor should be off and the delta contractor should become on. It should be noted that the main contractor should always be on.

You can also download the Star-delta PLC program from here.
In the next post we will be discussing the electrical wiring of a star delta starter. Also you can Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email for more PLC programming.
May 10, 2012
Omron Sysmac Studio Software
Omron Sysmac Studio is Omron's latest programming software for motion, drives and vision and supports Ladder programming, Structured Text and Function Block programming with a rich instruction set. Some of it common function are EtherCAT Configuration and Setup, CPU/Expansion Rack Configuration and setup, Motion Control setup, I/O Map Settings, Programming ladder diagrams, Programming structured text etc etc. This software is not good and compatible for machine having low disk space or very old PC as it require some higher configuration PC machine. Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.

The Sysmac Studio provides an integrated development environment to set up, program, debug, and maintain NJ-series Controllers and other Machine Automation Controllers, as well as EtherCAT slaves. Its standard version comes with 1, 3, 10, 30 & 50 Licenses in a DVD format.
Nov 4, 2011
Omron PLC Instruction for Serial Communication
We have discussed much about omron plc and programming with Omron plc. We have also studied about sample programs using omron PLC. Today we are going to study about the serial communication (No Protocol Mode) instruction. In cases where we need to connect a modem with PLC then we have to take the modem data by serial RS232 port. In this case no special protocol is used for communication and we have to use the Instruction for receiving and sending the data over serial RS232 channel.
Sending data to terminal device over RS232 Port :-
In omron PLC there is instruction named TXD by which we can send the specified number of bits to the device connected with PLC RS232 port.
Syntax of TXD Instruction :-
TXD S C N
where - S is the source word which contains the data to be transmitted. C is the control word and N is the number of bytes.
Now let us see that what the control word means and what its bit signifies. Control word is of 2 bytes i.e 16 bit. See the below diagram.
After writing this instruction we also have to ON a internal PLC bit to use this instruction to send the Data in No protocol mode.
If CPU Unit's built-in RS-232C Port is used than ON A392.05 when data need to be sent in the no-protocol mode. If Serial Option Board port is used than ON A392.13 when data can be sent in the no-protocol mode.
Also we have to define in the programming that we are going to use the RS232 port for the no protocol mode. for this we have to made certain settings in the CX-Programmer. See the below diagram.
RXD instruction for Receving data in NO Protocol Mode in Omron PLC :-
Similarly RXD instruction is used for receiving the data from the terminal device.
RXD D C N
Where D is the destination word and C, N are the same as in TXD instruction.
The auxiliary PLC internal bit A392.06 is on when no-protocol reception is completed.
Number of Receive Bytes Specified: The flag will turn ON when the specified number of bytes has been received. End Code Specified: The flag will turn ON when the end code is received or when 256 bytes have been received.
Keep reading for the latest tips and logic development using Omron PLC.
Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
Oct 22, 2011
Delta Released WPLSoft 2.20.11 Latest Version
As we all know that WPL Soft is used for the programming of delta series of PLC. In fact every Delta PLC can be programmed by two software either WPL Soft or ISP Soft. Delta recently launched the Updated version of WPL SOft. In this new version some features are added and some shortcuts are alo replaced. Also the amount of Data monitoring has been increased up to 256 data that can be monitored at a single time.
Delta PLC Latest Programming Software :-
A lot of new features like "Load Cell Module" button has been added. CP2000 model is also added in the library of PLC. Now CP2000 can be programmed using the WPL Soft 2.20.11 version. Also the Compiler settings option has been also added in this new version of WPL Soft. To provide a good look to the programming environment a option for changing the background colour of the "Ladder Diagram" has been added in the set colour of fonts and ladder. So overall this updated version has got some good features from the previous version of WPL Soft.
How to get Latest WPLSoft 2.20.11 Version Software :-
Yes as always Delta provides its software for free to all its customers , this time you can download it for free from Delta website or alternatively you can download it from below.
Get WPLSoft 2.20.11
Also you can subscribe to get all latest updates about Delta PLC and VFD.
Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
Aug 14, 2011
How to Find Square Root in PLC Programming
Dealing with the Process Parameters and Processing them is an integral part while making PLC Program for High End Process Application. Sometimes it happens that we need to find out the Square Root of a Particular Data. Omron PLC has got a very useful instruction for this purpose and we can directly calculate the Square root of a Value.Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
Calculate Square Root of A Value in Omron PLC :-
Square Root of a particular Data Word can be directly calculated in Omron PLC with a simple instruction. The name of instruction is ROOT.
Syntax :- ROOT S R
Where :- S is the Source Data Word whose Square Root is to be calculated and R is the Result Data word where the result will be stored.
This Instruction computes the square root of the eight-digit contents of Sq and Sq+1 and places the result in R. The fractional portion is truncated.
The value of square root will be calculated according to the data present in following Data Word as shown in Below Picture.

This instruction is very useful in handling and processing of Process Data.
We have also made a simple program for your reference.
Square Root Calculation PLC Program.
Aug 10, 2011
Find Avg Value Of Data In PLC - Omron PLC Programming
While doing PLC Programming for applications where we have to deal with data a lot , and we have to make calculations. In Process Automation Applications we have to show a lot of Data on SCADA and there we have to do much calculations. If we have to find the average value of some data word , then we have to write a very long ladder logic for that. But in Omron PLC there is one Instruction through which we can Directly get the average value of a particular Data Word or some process Parameter.
Calculating Average Value in Omron PLC Programming :-
In dealing with Process Parameters, where we have to show many parameters on the SCADA we have to deal with many calculations. Suppose that we want to show the average hours of DG Running hours per month or Average Tank Level then OMRON PLC provide a very useful instruction AVG through which this can be easily achieved.
AVG Instruction in Omron PLC :-
Symbol :- AVG S N D
Where S - is the source word whose average value is to be found out. N - is the number of cycles for which the average value will be calculated. D is the Result word where the average value will be stored.
Every time the AVG Instruction is execute the contents of S are stored in D+2 to D+N+1 , for the first execution of AVG Instruction the value of S is stored in D+2 , for the second execution of Instruction the value of S is stored in D+3 and so on. When the Execution of Instruction reaches N times then the average value of D is stored in D.
NOTE :- N must be BCD from #0001 to #0064
Example :- Consider AVG D100 #4 D200
So when this instruction condition goes from off to on for first time then the value of D100 is stored in D202 , at Second execution it is stored in D203 , at third execution it is stored in D204 , at fourth execution it is stored in D204 and average value is also calculated and stored in D200.
We have also made a Sample PLC Program using AVG Instruction for better understanding of yours.
SAMPLE PLC PROGRAM FOR AVG INSTRUCTION.
If you have any doubt regarding this , you can write us in comment section. We will be glad to help you.
Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
Aug 9, 2011
How To Connect Encoder With Delta DVP SS PLC
Encoder Interfacing with a PLC is very simple , but sometimes it becomes difficult if we are new to some PLC. Delta PLC are capable of reading encoder pulses through the available hardware and software counters in the PLC. So today we will see that how to read encoder pulses in Delta PLC. Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.
How To Connect Encoder With Delta DVP SS PLC :-
In Many applications we need to connect encoder with PLC for feedback purpose. There are many types of encoder available in market. Previously we have seen how can we connect Encoder with Omron PLC ,today we will see that how to make connections between a delta dvp plc and encoder.Also we see the required plc programming for this.
Hardware Connections between the Encoder and Delta DVP SS PLC :-
For making the connection we have to connect the A and B Phase output of the encoder to Input terminal x0 and x1 respectively. This can be simple connected , here in this case we are considering the two phase , so we will be able to get pulses in both CW and CCW rotation of Encoder shaft.
PLC Programming of Delta DVP SS for Encoder Interfacing :-
In Delta PLC there are hardware counters defined for reading the encoder pulses in the PLC Program.Considering the case of DVP 14SS here , the Hardware Counter 251 will be used for reading the encoder pulses at input x0 and x1. Suppose that we have connected a Encoder of PPR 5000 , then we will get 5000 pulses in 1 revolution of encoder shaft. The pulses will decrease if the encoder shaft is rotated in CCW Direction.
Sample PLC Program of Delta PLC Enncoder Interfacing :-
We have made a simple program of encoder interfacing with Delta DVP 14ss PLC , in this the same is done as discussed above. You can Download it for your reference.
PLC PROGRAM ENCODER DELTA PLC
Jul 10, 2011
Use P_ON and P_OFF in Omron PLC Programming
In the Omron PLC we have got two system Flags for Permanently On and Permanently Off Conditions. These PLC Bits Proves Very Useful while Troubleshooting the PLC Program. Generally after making the complete plc program when we commission the PLC Panel at site then at that time we need to test many things , so these bits make the task much easier.
How to Use P_on and P_off on Omron PLC :-
In our earlier tutorial we have already understood about the the PLC Internal Memory System Bits. When we make the PLC Program at a earlier stage of development than we have to include all the function and logic in it . But at the later stage we have to cut something out of it or add new logic and program sections.
Suppose that if we want that a particular rung condition should always be true , thus in this case we can use P_ON system flag.
Also while troubleshooting the PLC program if we want to cut the on condition of certain rung than we can use P_off.
To use the P_on and P_off in omron PLC , just input a contact and then select down from the options. Also you can enter the address directly.For P_On the address is CF113 and for P_Off it is CF114. See the Below Picture.

Also we have attached a sample PLC Program containing the P_on and P_Off.
PLC Program For use OF P_on and P_Off.
If you have any problem in PLC Programming related to Omron or Delta or Schneider PLC than you can write us in comment section and we will help you definitely.Subscribe to Automation-Talk by Email.













